What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes also known as K8s, is an open-source Container Management tool
It provides a container runtime, container orchestration, container-centric
infrastructure orchestration, self-healing mechanisms, service discovery, load balancing and container (de)scaling.
Initially developed by Google, for managing containerized applications in a cluster
environment but later donated to CNCF
Written in Golang
Kubernetes Architecture
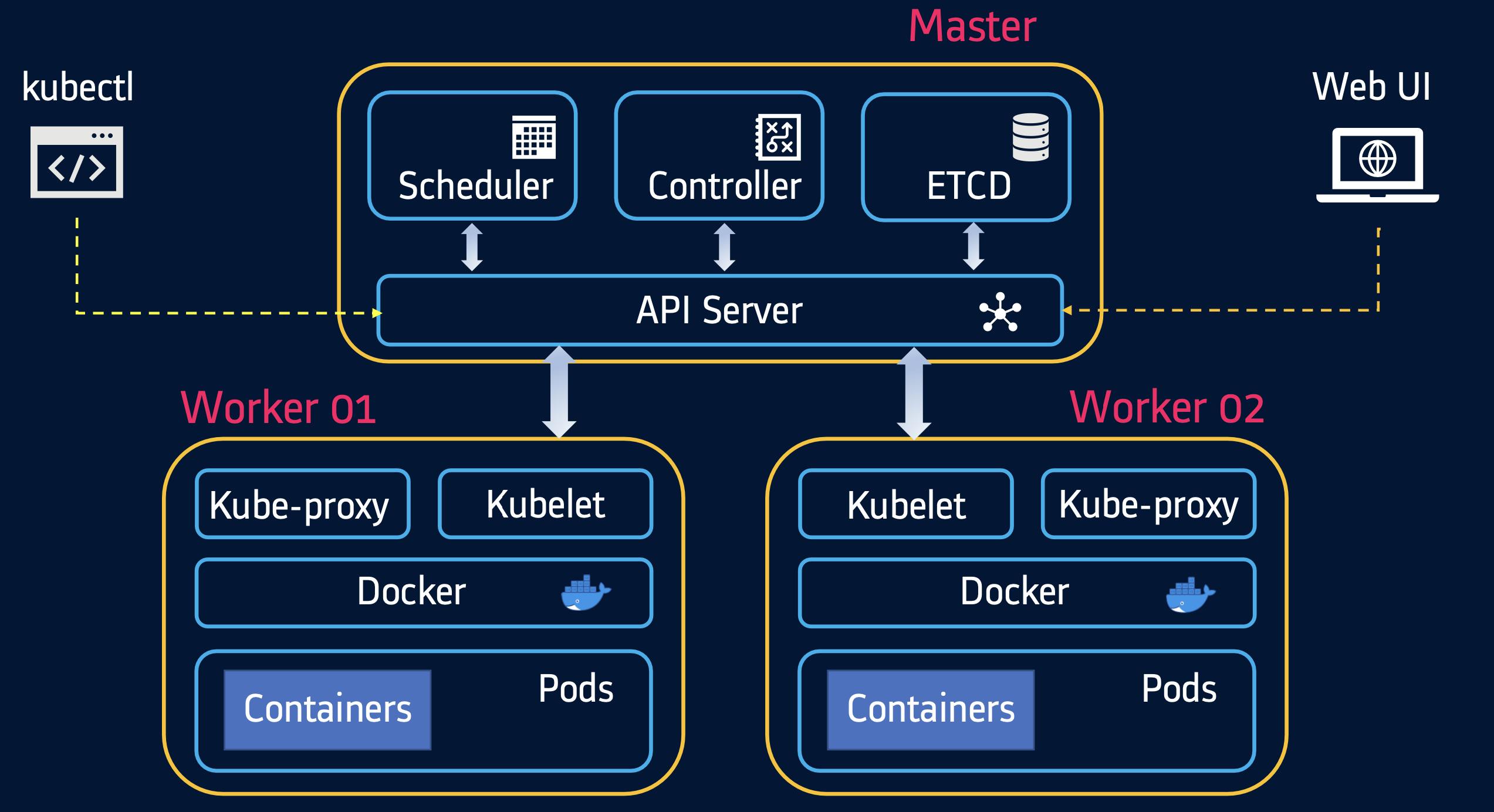
Kubernetes Master
Master is responsible for managing the complete cluster.
You can access master node via the CLI, GUI, or API
The master watches over the nodes in the cluster and is responsible for the actual orchestration of containers on the worker nodes
It is the access point from which administrators and other users interact with the cluster to manage the scheduling and deployment of containers.
It has four components: ETCD, Scheduler, Controller and API Server
1 - ETCD
ETCD is a distributed reliable key-value store used by Kubernetes to store all data used to manage the cluster.
When you have multiple nodes and multiple masters in your cluster, etcd stores all that information on all the nodes in the cluster in a distributed manner.
ETCD is responsible for implementing locks within the cluster to ensure there are no conflicts between the Masters
2 - Scheduler
The scheduler is responsible for distributing work or containers across multiple nodes.
It looks for newly created containers and assigns them to Nodes.
3 - API server manager
Masters communicate with the rest of the cluster through the kube-apiserver, the main access point to the control plane.
It validates and executes user’s REST commands
kube-apiserver also makes sure that configurations in etcd
match with configurations of containers deployed in the cluster.
4 - Controller manager
The controllers are the brain behind orchestration.
They are responsible for noticing and responding when nodes, containers or endpoints go down. The controllers make decisions to bring up new containers in such cases.
The kube-controller-manager runs control loops that manage the state of the cluster by checking if the required deployments, replicas, and nodes are running in the cluster
5 - Kubectl
kubectl is the command line utility using which we can interact with k8s cluster
Uses APIs provided by API server to interact.
Also known as the kube command line tool or kubectl or kube control.
Used to deploy and manage applications on a Kubernetes
Kubernetes Worker
- runs your containerized applications
1 - Kubelet
Worker nodes have the kubelet agent that is responsible for interacting with the master to provide health information of the worker node
To carry out actions requested by the master on the worker nodes.
2 - Kube proxy
- The kube-proxy is responsible for ensuring network traffic is routed properly to internal and external services as required and is based on the rules defined by network policies in kube-controller-manager and other custom controllers.
Installing Kubeadm: How to Set Up a Kubernetes Cluster
Requirements:
Two machines running Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, one for the master and one worker node.
The master node requires a minimum 2 vCPU and 4 GB memory. Select t2.medium instance type.
Sudo privileges are required on both machines.
Step - 1 : Install docker version on Both Master & Worker Node
sudo apt update -y sudo apt install docker.io -y sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable docker
Step - 2 : Install Kubernetes Components on Both Nodes
sudo curl -fsSLo /usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/kubernetes-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list sudo apt update -y sudo apt install kubeadm=1.20.0-00 kubectl=1.20.0-00 kubelet=1.20.0-00 -y
Step - 3: Configure Master Node
sudo su kubeadm init mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config kubectl apply -f https://github.com/weaveworks/weave/releases/download/v2.8.1/weave-daemonset-k8s.yaml kubeadm token create --print-join-commandThe kubeadm init command initializes the master node.
The mkdir command creates a directory for the Kubernetes configuration file.
The cp and chown commands copy the configuration file and set the correct permissions.
The kubectl apply command installs Weave Net, which is a popular networking plugin for Kubernetes.
The kubeadm token create command creates a token for joining worker nodes to the cluster.
Step - 4: Configure the Worker Node & Join to Master Node
sudo su kubeadm reset pre-flight checks # Paste the Join command on worker node with `--v=5`The kubeadm reset pre-flight checks command checks if the system meets the requirements for joining the Kubernetes cluster.
Then, paste the kubeadm token create command output from the master node on the worker node with the --v=5 flag. This joins the worker node to the Kubernetes cluster.
Step - 5 : Verify Nodes from Master
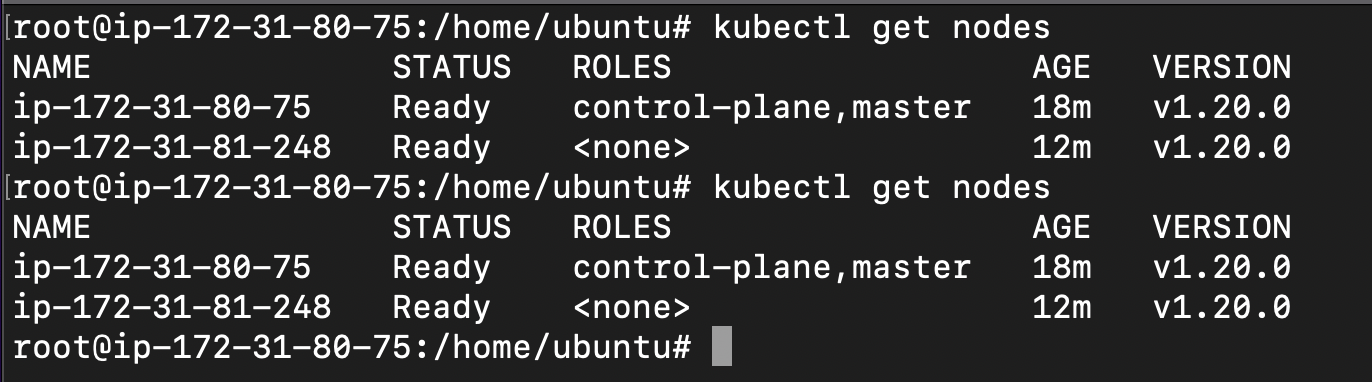
- This command will list down the nodes, if everything is setup correctly.
Thanks For Reading 😊
Happy Learing
Vishal Ranmale
