Deployment
A Deployment provides declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
You describe a desired state in a Deployment, and the Deployment Controller changes the actual state to the desired state at a controlled rate.
It seems similar to ReplicaSets but with advanced functions
Deployment is the recommended way to deploy a pod or ReplicaSets
By default Kubernetes performs deployments in rolling update strategy.
Below are some of the key features of deployment:
Easily deploy a ReplicaSets
Rolling updates pods
Rollback to previous deployment versions ✓ Scale deployment
Pause and resume deployment
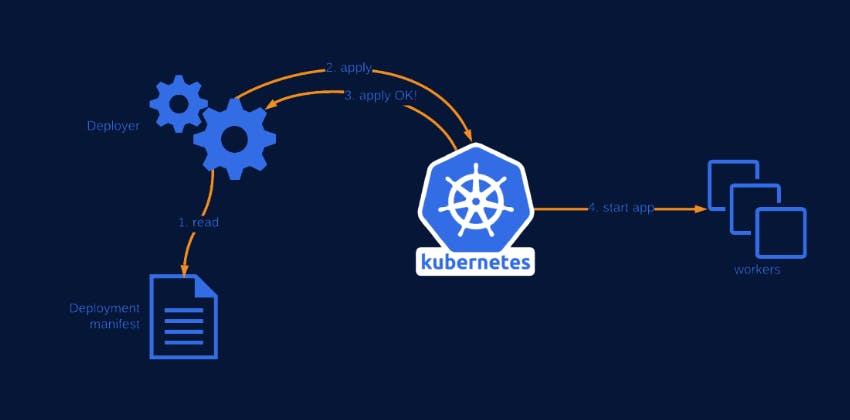
Deployment Strategy
Whenever we create a new deployment, K8s triggers a Rollout.
Rollout is the process of gradually deploying or upgrading your application containers.
For every rollout/upgrade, version history will be created, which helps in rolling back to the working version in case of an update failure
In Kubernetes, there are a few different ways to release updates to an application
Recreate: terminate the old version and release the new one. Application experiences downtime.
RollingUpdate: release a new version in a rolling update fashion, one after the other. It’s the
default strategy in K8s. No application downtime is required.
Blue/green: release a new version alongside the old version then switch traffic
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Deploy Django App on Kubernetes Cluster
Create a namespace to deploy django app & create deployment.yaml
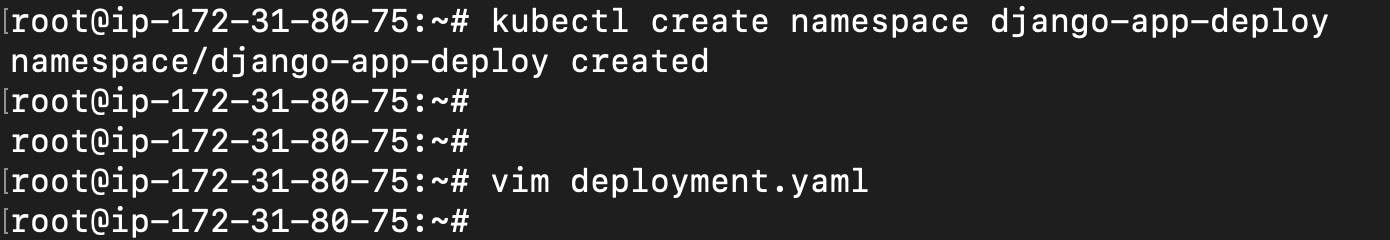
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: todo-deployment namespace: django-app-deploy labels: app: todo-app spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: todo-app template: metadata: labels: app: todo-app spec: containers: - name: todo-app image: trainwithshubham/django-todo:latest ports: - containerPort: 8000Check pods in namespace "django-app-deploy"

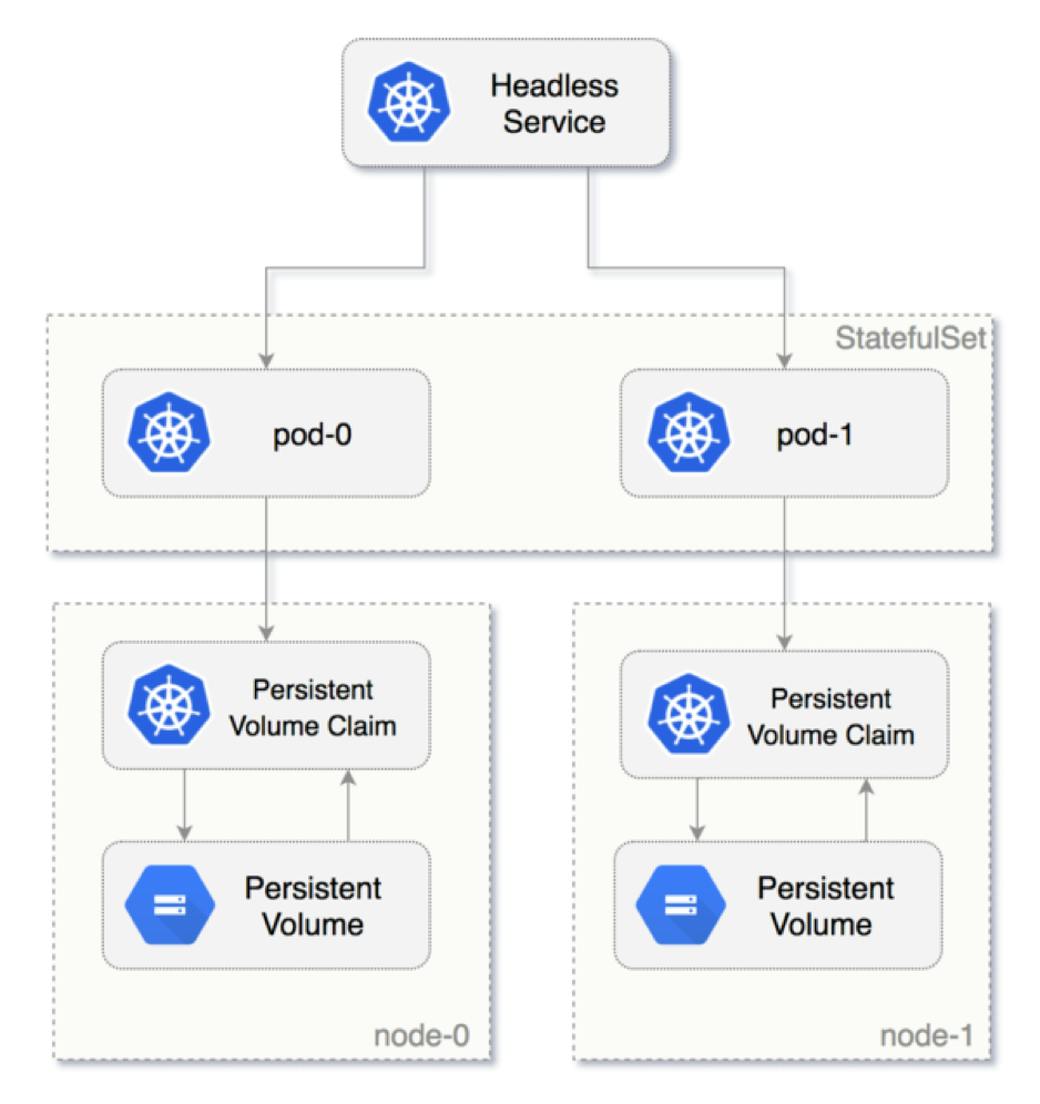
StatefulSets
StatefulSet is the workload API object used to manage stateful applications.
Manages the deployment and scaling of a set of Pods, and provides guarantees about the ordering and uniqueness of these Pods.
Like a Deployment, a StatefulSet manages Pods that are based on an identical container spec.
Unlike a Deployment, a StatefulSet maintains a sticky identity for each of its Pods.
These pods are created from the same spec, but are not interchangeable: each has a persistent identifier that it maintains across any rescheduling.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx # has to match .spec.template.metadata.labels
serviceName: "nginx"
replicas: 3 # by default is 1
minReadySeconds: 10 # by default is 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx # has to match .spec.selector.matchLabels
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
containers:
- name: nginx
image: registry.k8s.io/nginx-slim:0.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
storageClassName: "my-storage-class"
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
DaemonSets
A DaemonSet ensures that a specified collection of pods runs on the specified nodes. DaemonSet makes sure one pod exists per node.
Kubernetes DaemonSets can be used for various applications, including key-value stores, caches, and servers that require high availability, like messaging apps.
A DaemonSet will allow you to specify how many instances your app should run in the cluster and guarantee a consistent state among all pods running in the cluster.
Below are Some use cases for DaemonSet
1) Running a backup job You can have a DaemonSet running on every node in your cluster responsible for running backups of your etcd, MySQL data files, and PostgreSQL data files.
Logging Another use case is to install an agent such as Sysdig on each node and launch a DaemonSet to manage all of these agents in a cluster-ready state.
Enforcing network policy
Log aggregation

apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd
namespace: logging
labels:
app: fluentd-logging
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
name: fluentd
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: fluentd
spec:
containers:
- name: fluentd-elasticsearch
image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2
resources:
limits:
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
Jobs
A job creates one or more pods and ensures that a specified number of them successfully terminate.
Jobs can be used to reliably run a Pod to complete the specified number of times.
Pods in a Job can only use Never or OnFailure as their RestartPolicy.
Jobs can be used for tasks such as batch processing, data migration, or backups.
CronJobs can create Jobs once or repeatedly at specified times
Use Cases
Backup Jobs
Data processing tasks
Indexing tasks
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: pi
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: pi
image: perl:5.34.0
command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"]
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 4
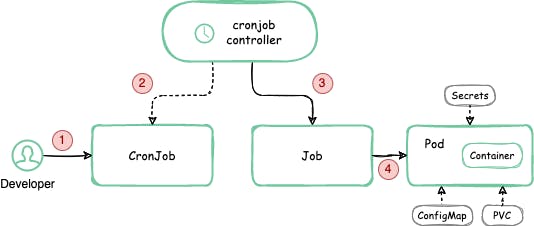
Cronjob
A Kubernetes Job is a workload controller object that performs specific tasks on a cluster. It differs from most controller objects such as Deployments and ReplicaSets, which need to constantly reconcile the current state of the cluster with a desired configuration.
A Job has a much more limited function: it runs pods until they complete a specified task, and then terminates them.
A CronJob is the same as a regular Job, only it creates jobs on a schedule (with a syntax similar to the Linux cron utility).
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: pi spec: template: spec: containers: - name: pi image: perl:5.34.0 command: ["perl", "-Mbignum=bpi", "-wle", "print bpi(2000)"] restartPolicy: Never backoffLimit: 4
Thank You 😊
Happy Learning 📚
Vishal Ranmale
